As we enter a new year, and a new phase of the Covid-19 pandemic, we are reminded of the need to follow public health advice to stop the spread of the virus. The emergence of new variants of Covid-19, which appear to be more transmissible, has resulted in tougher restrictions across the world. Although the emergence of new variants of Covid-19 can seem frightening, we are not powerless in preventing the spread of the virus; face coverings, social distancing, regular handwashing and self-isolating remain effective.
Additionally, the development and subsequent roll-out of numerous vaccines should provide us all with hope that there is light at the end of the tunnel. However, although vaccines appear to protect people from becoming seriously ill with the virus, there is still uncertainty regarding the impact vaccines will have on viral transmission of Covid-19.
Therefore, the need for those with symptoms to self-isolate, get tested and undergo contact tracing when a positive case is detected is likely to remain. This will become even more important in the months ahead, as we see the gradual re-opening of hospitality, leisure and tourism sectors.
Effectiveness of contact tracing
Contact tracing is a tried-and-tested public health intervention intended to identify individuals who may have been in contact with an infected person and advise them to take action that will disrupt chains of transmission. Prior to Covid-19, contact tracing was often used to prevent the spread of sexually transmitted infections, and has been heralded as vital to the eradication of smallpox in the UK.
According to modelling, published by the Lancet Infectious Diseases, a combination of self-isolation, effective contact tracing and social distancing measures, may be the most effective and efficient way to control the spread of Covid-19.
However, for contact tracing to be at its most effective, the modelling estimates that for every 1,000 new symptomatic cases, 15,000 to 41,000 contacts would have to be asked to self-isolate. Clearly, the logistical burden of operating a manual contract tracing system is high. As a result, governments have chosen to augment existing systems through the deployment of digital contract tracing apps, which are predominantly built using software developed by Apple and Google.
Digital contact tracing
As we go about our day-to-day lives, especially as restrictions are eased, it may not be possible to name everyone you have encountered over the previous 14 days if you later contract Covid-19. Digital contact tracing provides a solution to this issue by harnessing the Bluetooth technology within our phones to help identify and remember potential close contacts. Research by the University of Glasgow has found that contact tracing apps can contribute substantially to reducing infection rates when accompanied by a sufficient testing capability.
Most countries have opted to utilise a system developed by Apple and Google, known as Exposure Notifications, as the basis for digital contact tracing. Public health authorities have the option to either provide Apple and Google with the criteria which defines when an alert should be generated or develop their own app, such as the Scottish Government’s Protect Scotland.
Exposure notification system
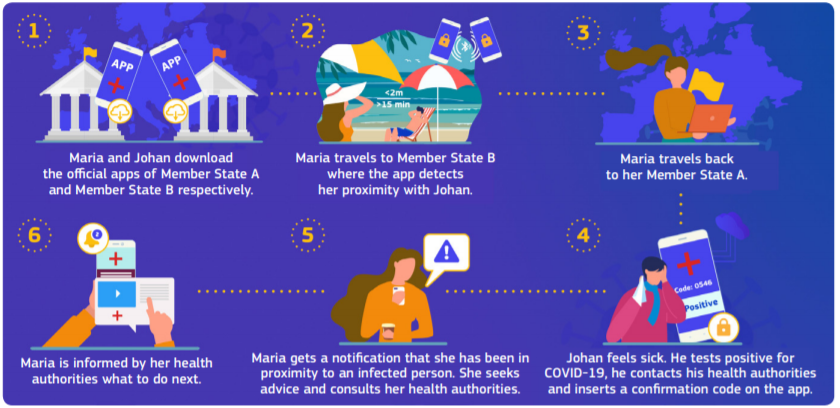
In order to protect privacy, the exposure notification system can only be activated by a user after they have agreed to the terms; the system cannot be unilaterally activated by public health authorities or Apple and Google.
Once activated, the system utilises Bluetooth technology to swap anonymised IDs with other users’ devices when they come into close contact. This has been described as an anonymous handshake. Public health authorities set what is considered as a close contact (usually contact at less than a 2-metre distance for over 15 minutes), and the app calculates proximity measurements over a 24-hour period.
Anonymised IDs are not associated with a user’s identity, change every 10-20 minutes and collected anonymised IDs are securely stored locally on user devices for a 14-day period (incubation period of Covid-19) before being deleted.
If a user tests positive for Covid-19, the public health authority will provide them with a code that confirms their positive diagnosis. This will then provide users with an option to upload collected anonymous IDs to a secure public health authority server. At least once a day, the user’s phone will check-in with this server to check if any of the anonymised IDs collected in the previous 14-days match up with a positive case. If there is a match, and the proximity criteria has been met, a user may receive a notification informing them of the need to self-isolate.
Analysis conducted by the National Institute for Health Research highlights that the use of contact tracing apps, in combination with manual contact tracing, could lead to a reduction in the number of secondary Covid-19 infections. Additionally, the analysis revealed that contact tracing apps identified more possible close contacts and reduced the amount of time it took to complete contact tracing. The analysis concluded that the benefits of digital contact tracing include the ability to trace contacts who may not be known to the infected individual and the overall reliability and security of digitally stored data, rather than an individual’s memory or diary.
Therefore, it could be said that digital contract tracing apps will be most effective when restrictions ease and we are more likely to be in settings where we may be in close contact with people we may not know, for example, when we’re on holiday or in a restaurant.
Cross-border handshakes
Covid-19 naturally does not respect any form of border, and as restrictions on domestic and international travel are relaxed, opportunities will arise for Coivd-19 to spread. In order to facilitate the reopening of the tourism sector, there have been calls for countries which have utilised the Exposure Notification system to enable these systems to interact.
Examples of interoperability already exist internally within the UK, as an agreement exists between Scotland, England and Wales, Northern Ireland, (plus Jersey, Guernsey and Gibraltar), that enables users to continue to receive exposure notifications when they visit an area they do not live in, without the need to download the local public health authority app.
Additionally, the European Union has also developed interoperability of the Exposure Notification system between member states, with a commitment to link 18 national contact tracing apps, establishing the world’s largest bloc of digital contact tracing. The EU views the deployment of linked apps as vital to re-establishing safe free movement of people between member states, for work as well as tourism.
Over the next few months, it is likely that links will be created across jurisdictions. For example, the Scottish Government has committed to investigating how interoperability can be achieved between the Scottish and EU systems. The interoperability of Northern Ireland and Ireland’s contact tracing app highlights that on a technical level there appears to be no barrier for this form of cross-jurisdiction interaction.
Therefore, as restrictions ease, the interoperability of digital contact tracing apps may become a vital way in which to ensure safe travel, as we learn to live with the ongoing threat of Covid-19.
Final thoughts
Covid-19 has proven itself to be a persistent threat to our everyday lives. However, the deployment of effective vaccines provides us with hope that the threat will be minimized soon. Until then, the need to utilise contact tracing is likely to remain.
As the roll-out of mass-vaccination programmes accelerates, and restrictions are relaxed, we are likely to be in more situations where we will be in contact with more people, not all of whom we may necessarily know. This will be especially true as domestic and international tourism begins to re-open. In these scenarios, the Exposure Notification system, and interoperability between public health authority apps, will become increasingly vital to the operation of an effective contact tracing system.
In short, digital contact tracing may prove to be key to the safe re-opening of the tourism sector and enable users to easily and securely be contact traced across borders.
Follow us on Twitter to see which topics are interesting our research team.
Further reading: articles on COVID-19 and digital from The Knowledge Exchange blog
Share
Related Posts
Supporting residents on the decarbonisation journey: leveraging data for effective retrofit projects
As the drive towards decarbonisation intensifies, the social housing sector’s ability to collect, store and manage vast amounts of data becomes increasingly critical. With a shared goal of creating warmer, carbon-free homes, housing associations’ strategic use of data is essential ....
By Donna Gardiner While free school meals (FSM) have been available in England on a means-tested basis since 1944, recent years have seen a renewed focus upon the potential benefits of providing free school meals to all school-aged children. Currently, ....
Today sees the start of Community Garden Week 2023. Across the UK, communities will be celebrating the many and varied types of community gardens, from children’s and neighbourhood gardens to therapy gardens and allotments. The benefits of community gardens are ....
By Hollie Wilson At the start of 2020, an independent review was published setting out what needed to be done to bring about changes to the care system for children and young people in Scotland. At the heart of the ....