Chart by Economic Research Council
By Stacey Dingwall
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) has released its second annual update on the number of people employed on zero hours contracts, which suggests that in August 2014 UK firms were employing 1.8 million people on such contracts.
What is a zero hours contract?
According to Acas, the term ‘zero hour contract’ (although not defined in legislation) can be understood as “an employment contract between an employer and a worker, which means the employer is not obliged to provide the worker with any minimum working hours, and the worker is not obliged to accept any of the hours offered”.
Use of the contracts has been a highly controversial issue in recent months, with high-profile retailers such as Sports Direct (who employ 90% of their part time staff on zero hours contracts) coming in for criticism of their “exploitation” of their employees. The sports retailer is also facing legal action from hundreds of their workers due to their exclusion from the company bonus scheme, thanks to the nature of their contracts.
Increasing or not?
The ONS’ first Analysis of Employee Contracts that do not Guarantee a Minimum Number of Hours found that between January and February 2014, 1.4 million UK workers were employed on zero hours contracts. Despite the inevitable headlines depicting the new figure as a direct increase from the 2014 analysis, the ONS was careful to warn against this in its latest analysis, noting that it covers a different time of year than the first release therefore the number of contracts reported may be affected by seasonal factors.
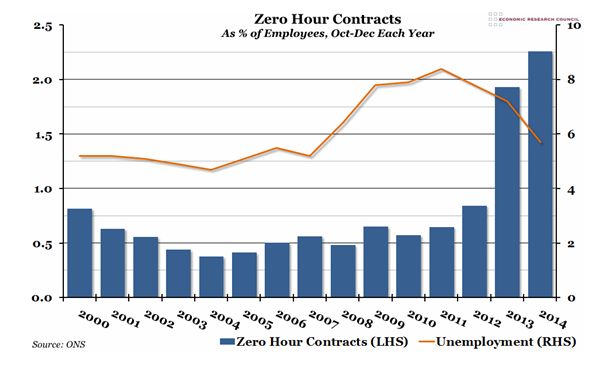
The latest release also includes data from the Labour Force Survey (LFS), which indicates that the number of people employed on zero hours contracts in their main employment, between October and December 2014, was 697,000 or 2.3% of all people in employment. The figure for the same period the year before was 586,000 or 1.9% of people in employment although again, the ONS are careful to stipulate that they can’t be certain how much of this ‘increase’ is due to greater recognition of what constitutes a zero hours contract, as opposed to new contracts.
The Economic Research Council suggested that a lot of the jobs that have been created recently have come with much less security and guaranteed pay. And the UK Commission for Employment and Skills have noted that 33% of people on zero hour contracts would like to work more hours (either in their current job or in a different one), compared to just 13% of people not on a zero hour contract.
Zero hours and the general election
The issue of the use of zero hours contracts looks set to become a key feature of parties’ campaigns in the upcoming general election. Current Secretary of Business, Innovation and Skills – Liberal Democrat Vince Cable – has already put forward legislation (clause 151 of the Small Business Enterprise and Employment Bill, currently before the House of Lords) which would see exclusivity clauses in contracts (which prevent those employed on zero hours contracts from seeking additional work to supplement their income) banned.
The Conservative Work and Pensions Secretary, Iain Duncan Smith, has however defended the contracts, arguing that they “provide people with a flexible way of working and the freedom to arrange jobs around other commitments” and “allow employers to be competitive in response to market trends”.
What of the other parties? Labour has vowed to “end exploitative zero hours contracts” and introduce “new rights” to employees on such contracts, however has stopped short of proposing to ban employers from offering them altogether. Somewhat embarrassingly for the party, figures released by the Independent Parliamentary Standards Authority (IPSA) and seized on by the tabloids, have indicated that over 30 Labour MPs employed staff on zero hours contracts in 2014.
The Green Party is firmly against the use of zero hours contracts altogether: leader Natalie Bennett has been calling on the government to place an outright ban on them since 2013. UKIP leader Nigel Farage has also criticised the long-term use of zero hours contracts by employers, and has called for large employers to be subject to a code of conduct as to how they are applied.
Zero hours contracts aren’t a financial necessity
In these times of budget cuts, many local authorities have argued that they have no choice but to offer some of their workers zero hours contracts. One area in which this has been particularly prevalent is in the provision of social care, with some employees paid on a ‘time and task’ basis, i.e. only for the amount of time they actually spend with a client, which can be as little as 15 minutes in some cases.
In 2012, Southwark Council took the decision to move away from this approach, after feedback from care workers and service users indicated that it did not allow workers to carry out their duties with the required level of compassion. The Council carried out a review of their homecare services and found that extending the length of visits greatly helped in keeping service users healthy in their own homes and out of hospital and residential care. It also noted that the costs of providing longer visits had been ‘passed on’ to their care workforce over time through the use of zero hours contracts and, wishing to end this, announced that from October 2014 they would be eliminating their use altogether, and offering guaranteed hours of employment to their staff.
Immediate reaction to the release of the latest figures has been plentiful; it now remains to be seen whether it is reflected in party campaigns in the forthcoming general election.
The Idox Information Service has a wealth of research reports, articles and case studies on zero hours contracts and other employment issues. Items of interest include:
The decent jobs deficit: the human cost of zero-hours working in the UK
Give and take? Unravelling the true nature of zero-hours contracts
Zero hours contract: not all bad news
Zero-hours contracts: myth and reality
Flexibility or insecurity? Exploring the rise in zero hours contracts
Share
Related Posts
A recent item on BBC Radio 4’s Today programme generated an unusually high number of responses from listeners. A man who had lost his job in the financial services sector at the age of 57 described his difficulty in trying ....
A recent survey by the Royal Town Planning Institute (RTPI) in July 2021 aimed to gauge UK public awareness of the planning profession. The results suggested a significant disconnect between the public perception of planning, the scope of professions in ....
It is well recognised that the UK faces a shortage in STEM (science, technology, engineering and maths) skills, and that at current projections, this gap in skills and knowledge is only going to grow in the coming years. Before the ....
Yesterday marked the 111th International Women’s Day, a global day of celebration for the social, economic, cultural and political achievements of women. But it is also an opportunity to reflect on and further the push towards gender equality. While there ....
